Architectural Achievements
The Taj Mahal

The Taj Mahal is the most famous example of Mughal architecture and a symbol of artistic excellence. Built by Emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his wife Mumtaz Mahal, it is known for its balance, elegance, and detailed decoration. Constructed from white marble and decorated with precious stone inlay work, the monument combines Persian, Indian, and Central Asian design elements.
Its large dome, symmetrical layout, and surrounding gardens reflect Mughal mastery of engineering and aesthetics. Today, the Taj Mahal stands as a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a global icon of architectural beauty.
The Red Fort
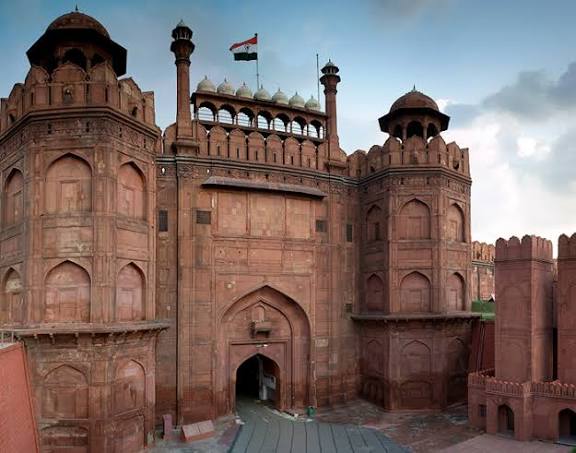

Another major Mughal monument is the Red Fort in Delhi, also commissioned by Shah Jahan. Built using red sandstone, it served as the political center of the empire. The fort contains impressive structures such as the Diwan-i-Aam (Hall of Public Audience), Diwan-i-Khas (Hall of Private Audience), and Rang Mahal.
The Red Fort reflects the grandeur and authority of Mughal rule through its massive walls, decorative halls, and carefully planned gardens. It remains a powerful symbol of India’s historical and cultural identity.
Artistic Contributions
Mughal Miniature Paintings
Mughal miniature paintings are among the most refined art forms developed during the empire. These paintings are known for their fine details, vibrant colors, and realistic depiction of people, animals, and nature. They often illustrated historical events, royal life, literary stories, and court scenes.
Artists worked with great precision, using layered techniques and natural pigments. The tradition flourished under rulers like Akbar, Jahangir, and Shah Jahan, who actively supported artists and workshops.
Calligraphy and Manuscripts
Calligraphy was highly respected in Mughal culture and was used extensively for religious texts, poetry, and official documents. Persian and Arabic scripts, especially Nastaliq and Naskh, were commonly used.
Mughal manuscripts were beautifully decorated with gold, floral patterns, and detailed borders. High-quality paper and materials were used to ensure durability. Many important historical and literary works were preserved through these manuscripts, highlighting the Mughals’ dedication to learning and scholarship.
Cultural Influence
Language and Literature
The Mughal period had a lasting impact on India’s linguistic development. Persian was the official language of administration and culture, influencing local languages. Over time, Urdu emerged as a new language formed from Persian, Arabic, Turkish, and Indian dialects.
Literature thrived during this period, including poetry, historical records, and prose. Important works such as the Akbarnama by Abul Fazl documented Mughal history, while later poets enriched Persian and Urdu literature.
Music and Dance
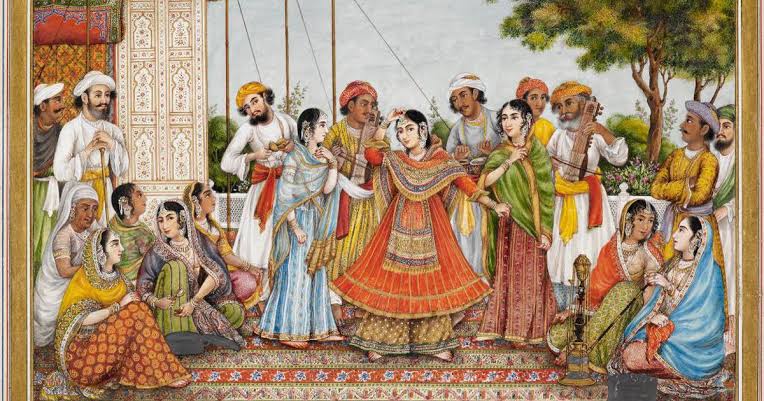

The Mughal courts were centers of musical innovation. Hindustani classical music developed further during this time, supported by royal patronage. Tansen, one of the greatest musicians in Indian history, served in Akbar’s court and contributed significantly to musical traditions.
Dance forms such as Kathak also gained prominence. This style blended Indian storytelling traditions with Persian influences, creating a refined classical dance that continues to be performed today.
Religious Tolerance
Mughal Religious Policies
Emperor Akbar is especially remembered for promoting religious tolerance through his policy of Sulh-e-Kul, meaning “peace for all.” He encouraged harmony among different religious groups and removed discriminatory taxes like the jizya on non-Muslims.
Akbar invited scholars from various religions to engage in discussions at his court. These interactions helped promote understanding, respect, and cooperation among diverse communities.
Impact on Society
The Mughal approach to religion encouraged cultural blending and reduced conflict. Artistic styles, language, and traditions were enriched through interaction among different faiths. This atmosphere of tolerance contributed to social stability and cultural growth across the empire.
Legacy and Preservation
Conservation of Mughal Monuments
Preserving Mughal heritage is essential for understanding India’s history. Major monuments such as the Taj Mahal, Red Fort, Humayun’s Tomb, and Fatehpur Sikri have undergone restoration and maintenance to protect their structure and beauty.
These conservation efforts ensure that future generations can continue to appreciate the architectural achievements of the Mughal era.
Promoting Mughal Culture
Museums, exhibitions, cultural festivals, and educational programs play an important role in keeping Mughal art and traditions alive. Research publications and academic studies further help spread awareness about the empire’s contributions.
Conclusion
The Mughal Empire left a deep and lasting mark on India through its architecture, art, culture, and policies of tolerance. Its monuments, artistic traditions, and cultural values continue to shape India’s identity. Preserving and promoting this heritage ensures that the achievements of the Mughal period remain an important part of world history.